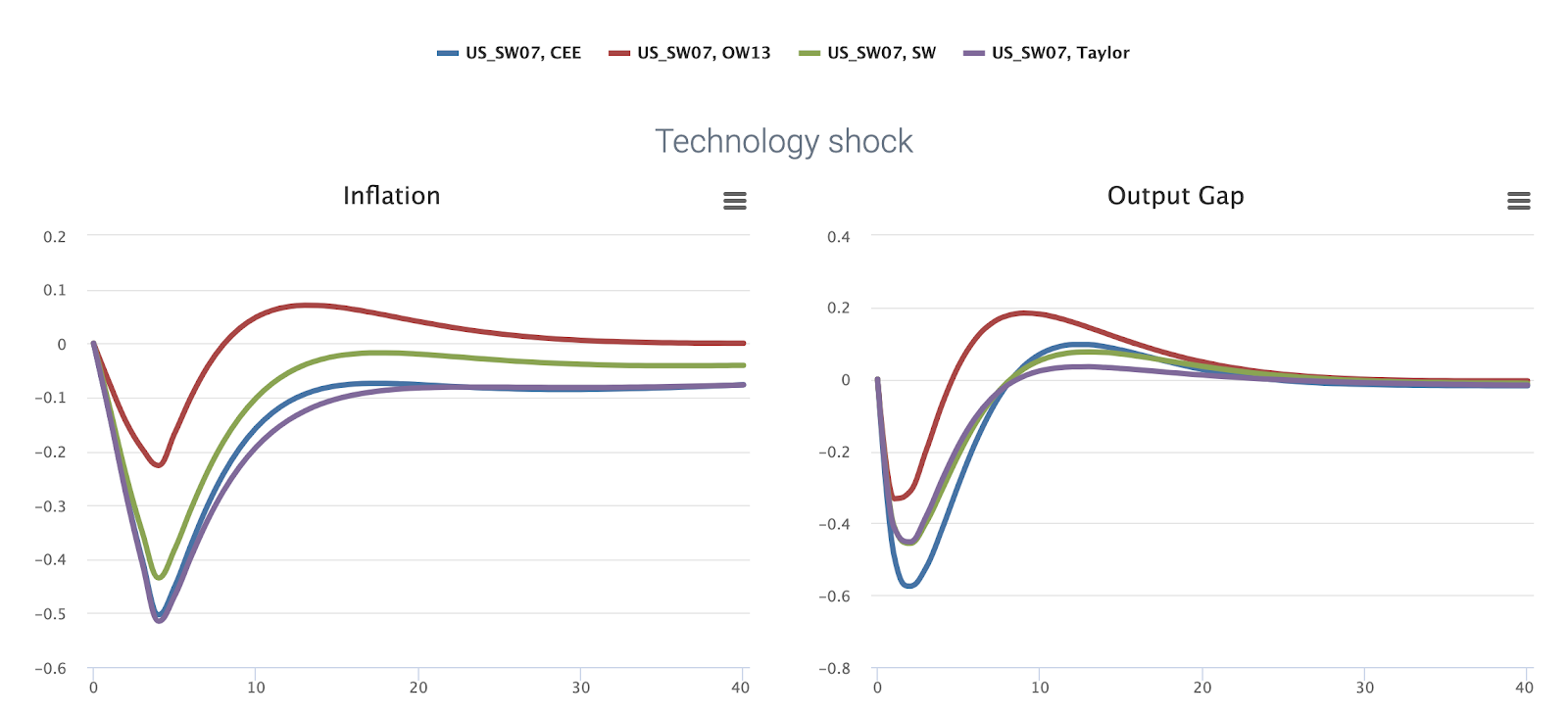
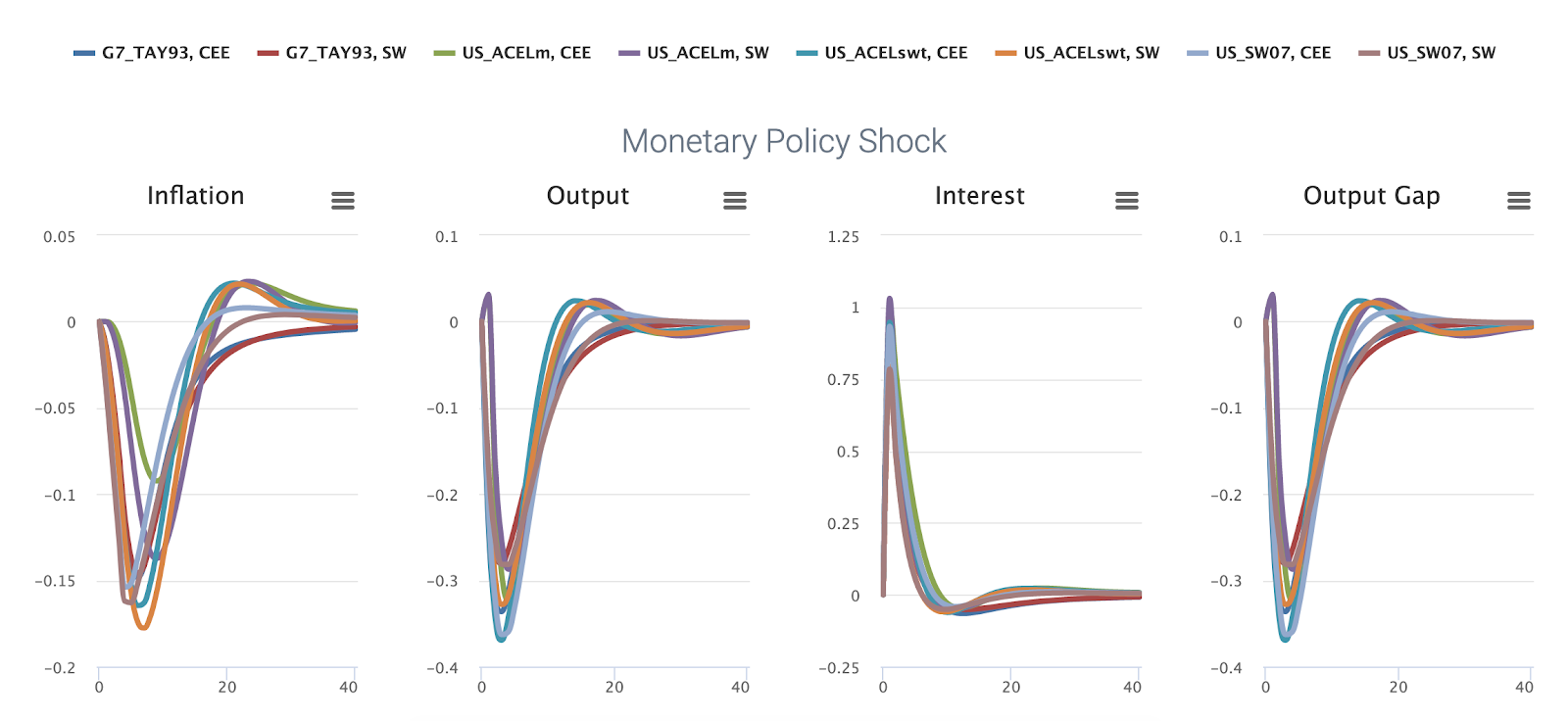
Could a central bank rely on the emerging 2nd generation NK models before the 2008 financial crisis?

Why is it interesting? The comparison shows that central banks have to deal with model uncertainty and that different models imply very different responses in key economic variables. Many central banks included second-generation New Keynesian models in their suite of models prior to the Great Recession, mainly due to the improved empirical fit of these models relative to the early small-scale models. What to do on the MMB? Models: NK_RW97, NK_IR04, US_ACELm, US_SW07 Policy Rules: Gerdesmeier & Roffia (2004) Shocks: Monetary Policy Shock Variables: Inflation, Interest, Output What is interesting? The impulse responses peak on impact, returning only slowly to their non-stochastic steady state values afterwards. This is at odds with empirical VAR evidence, which suggests that both output and inflation exhibit a hump-shaped response to a monetary policy shock. Medium-size DSGE models of the second generation induce such hump-shaped impulse responses by adding capit...